NMNs: A Breakthrough in Diabetes Management

Diabetes has become a global epidemic, affecting over 463 million adults worldwide, and the numbers are only expected to rise.
The condition, which involves chronic high blood sugar levels, can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss.
Traditional diabetes management strategies typically include medications like metformin, insulin therapy, and lifestyle changes focused on diet and exercise. While these treatments are effective for many, they may not be enough for everyone, and side effects can be a concern.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative approaches to diabetes management, with NMNs emerging as a promising option.
These compounds, which play a crucial role in cellular energy production and metabolism, have shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity and regulating glucose levels.
As research continues to unfold, NMNs could become a valuable tool in the fight against diabetes, offering a new avenue for managing high blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
In this article, we talk about…
- The role of NMNs in transforming diabetes management, particularly in enhancing blood sugar control and boosting insulin sensitivity.
- The potential of NMNs to significantly improve metabolic health and offer new support in the treatment of diabetes.
- Emerging research that positions NMNs as a potential game-changer in the future of diabetes care.
- Important dosage guidelines and safety considerations for maximizing the benefits of NMNs in diabetes management.
Understanding NMNs: An Overview
NMN is a naturally occurring compound found in the body. It is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic reactions, replenishing cellular NAD+ levels.
It is a molecule comprised of a nicotinamide base, a ribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
It can be found in various foods, such as broccoli, cabbage, and avocados, although the levels present in these sources are relatively low. NMN supplements are available in a more concentrated form.
Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, is not only known for its high nutritional value but also for containing NMN.
This compound, along with other beneficial nutrients, contributes to the overall health benefits of consuming broccoli.
Similarly, cabbage, another member of the cruciferous vegetable family, contains traces of NMN. Including these vegetables in your diet can provide a natural source of NMN, supporting your body’s NAD+ production.
Avocados, often praised for their healthy fats and creamy texture, also contain NMN. This fruit offers a delicious way to incorporate NMNs into your diet.
Avocados can contribute to your overall NMN intake, whether you enjoy it in salads, spreads, or smoothies.
The Role of NMN in the Body
NMN plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism.
As a precursor to NAD+, it serves as a vital component in the electron transport chain, facilitating the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the primary source of energy in cells.
Additionally, NMN is involved in the activation of sirtuins, a family of proteins linked to longevity and metabolic regulation.
The electron transport chain is a complex process that occurs within the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell.
NMN’s involvement in this chain ensures the efficient production of ATP, which fuels various cellular activities. This energy is essential for processes such as muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and maintaining overall cellular function.
Sirtuins, on the other hand, are a group of proteins known for their involvement in regulating cellular processes related to aging and metabolism.
NMN’s role in activating sirtuins highlights its potential impact on these processes. By supporting sirtuin activation, NMN may contribute to promoting healthy aging and metabolic balance.
Research into the potential benefits of NMN is ongoing, with scientists exploring its role in various aspects of health and well-being. From energy production to DNA repair and beyond, NMN continues to intrigue researchers and health enthusiasts alike.
The Connection Between NMN and Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. It can result from inadequate insulin production or impaired insulin sensitivity. B
Both types of diabetes, type 1 and type 21, present significant challenges in managing blood glucose levels effectively.
The Impact of Diabetes on the Body
Diabetes can lead to a wide range of complications, affecting various organs and systems in the body.
Prolonged hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a common complication of diabetes and refers to conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels.
High blood glucose levels can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to the formation of plaques and narrowing of the arteries. This can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy is another potential complication of diabetes.
It occurs when high blood glucose levels damage the nerves, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain in the affected areas. Diabetic neuropathy can affect various parts of the body, including the feet, legs, hands, and arms.
Nephropathy
Nephropathy, or diabetic kidney disease, is a condition that affects the kidneys. Prolonged hyperglycemia can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste products from the blood. This can eventually lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. High blood glucose levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This can result in vision problems and, if left untreated, may lead to blindness.
How NMN Interacts with Diabetes
NMN has shown potential in addressing several aspects of diabetes management. It has been studied for its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, increase energy metabolism, and regulate glucose levels in both preclinical and clinical settings.
Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively the body’s cells respond to insulin.
In individuals with diabetes, insulin sensitivity is often impaired, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
NMN has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity, allowing the cells to better utilize glucose for energy production.
Energy metabolism is the process by which the body converts nutrients into energy.
In individuals with diabetes, energy metabolism may be disrupted, leading to fatigue and reduced physical activity. NMN has been shown to boost energy metabolism, potentially alleviating symptoms of fatigue and improving overall energy levels.
Regulating glucose levels is crucial in diabetes management.
NMN have been found to influence glucose metabolism, helping to maintain stable blood glucose levels. By promoting glucose uptake and utilization, NMN may contribute to better glycemic control in individuals with diabetes.
Furthermore, NMN has been investigated for its potential role in preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes-related complications.
Studies have suggested that NMN may have protective effects on blood vessels, nerves, and organs, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
While the research on NMN and diabetes is still ongoing, the findings so far are promising.
NMN holds potential as a therapeutic agent for managing diabetes and mitigating its associated complications.
Further studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and determine the optimal dosage and administration of NMN in the context of diabetes treatment.
The Potential Benefits of NMN in Diabetes Management
Research suggests that NMN may offer several potential benefits for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. These benefits go beyond traditional diabetes management strategies and provide new avenues for improving overall health and well-being.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity with NMN
Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively cells respond to insulin signals to take up glucose from the bloodstream.
Impaired insulin sensitivity is a hallmark of diabetes and can contribute to elevated blood glucose levels. NMN has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity by increasing the activity of sirtuins, proteins that play a role in insulin signaling pathways.
When NMN is introduced into the body, it activates sirtuins, which in turn improve insulin sensitivity.
This means that cells become more responsive to insulin signals, allowing for better glucose uptake and utilization. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, NMN helps to regulate blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of hyperglycemia, a common complication of diabetes.
Furthermore, the increased activity of sirtuins also positively impacts other metabolic processes. It promotes the breakdown of fatty acids and inhibits the production of glucose by the liver, both of which are important for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing the progression of diabetes.
NMN and Glucose Levels: A Closer Look
Regulating blood glucose levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. NMN may help maintain glucose homeostasis by stimulating the production of NAD+, which is involved in cellular energy metabolism.
NAD+ activates pathways that enhance glucose uptake and utilization, reducing blood glucose levels.
When NAD+ levels are increased through NMN supplementation, the body’s ability to regulate glucose is improved.
This is achieved through the activation of key enzymes that are responsible for glucose metabolism. As a result, blood glucose levels are better controlled, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia and its associated complications.
Moreover, NMN also plays a role in preventing the development of insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin signals.
By promoting the production of NMN, it helps to maintain the integrity of insulin signaling pathways, ensuring that cells continue to respond effectively to insulin’s actions.
Additionally, NMN has been shown to have antioxidant properties, which can further benefit individuals with diabetes.
Oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them, is often elevated in diabetes.
By reducing oxidative stress, NMN helps to protect cells from damage and preserve their function, contributing to improved overall health.
The Science Behind NMN and Diabetes
Recent scientific studies have shed light on NMN’s potential in managing diabetes and its underlying mechanisms.
Recent Research on NMN and Diabetes
A study published in Cell Metabolism2. Volume 14, Issue 5, October 2011, pages 528-536, showed that NMN supplementation improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice.
Another study revealed that NMN administration enhanced mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in animal models of type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the Mechanisms of NMN in Diabetes Management
Studies have identified multiple mechanisms through which NMN may exert its positive effects on diabetes management.
These include its role in enhancing insulin signaling, promoting glucose uptake, improving mitochondrial function, and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Safety and Dosage of NMN for Diabetes
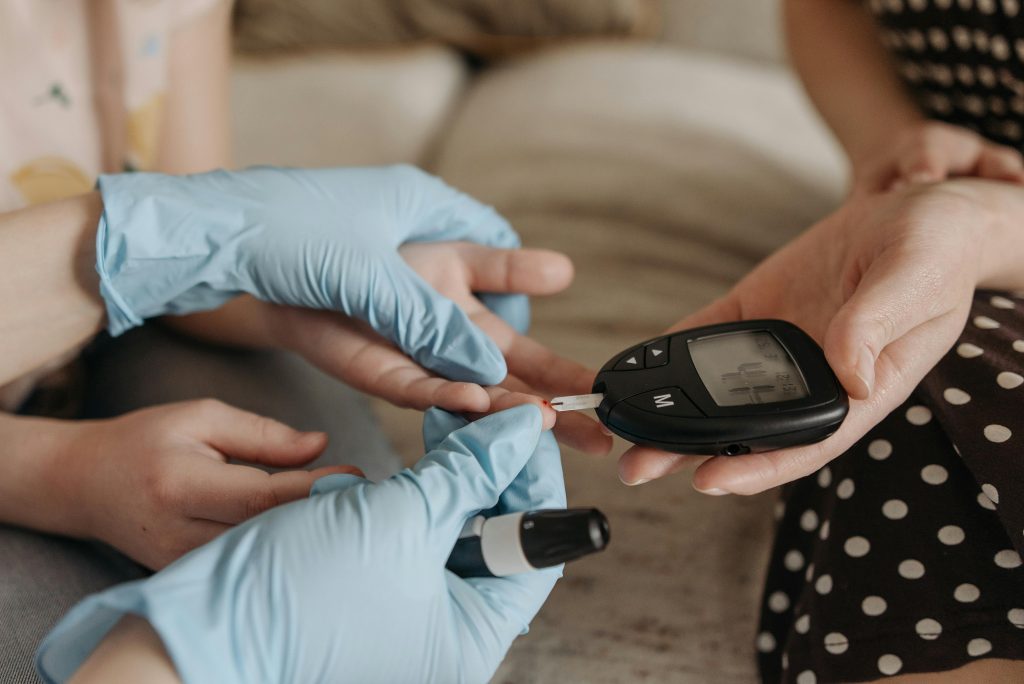
When considering any supplement, including NMN, it is essential to understand its safety profile and recommended dosage, especially for individuals with diabetes.
Recommended Dosage of NMN for Diabetic Patients
The optimal dosage of NMN for diabetes management has not been definitively established, as research in this area is ongoing. However, some studies suggest a daily dosage ranging from 250mg to 500mg for general health benefits.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting NMN supplementation, especially if you have diabetes or any other underlying medical condition.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Measures
NMN is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, potential side effects may include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea or diarrhea.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is recommended to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase over time. As individual responses may vary, consulting with a healthcare professional is advised.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NMN holds promise as a potential tool in diabetes management.
Its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate glucose levels, and enhance cellular energy metabolism makes it an area of interest for further research.
However, more studies are needed to better understand its long-term effects, optimal dosage, and potential interactions with other medications.
As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Increase your NAD+ levels with Jinfiniti Vitality Boost.
Take this groundbreaking nutritional supplement to increase your energy and improve sleep quality.




